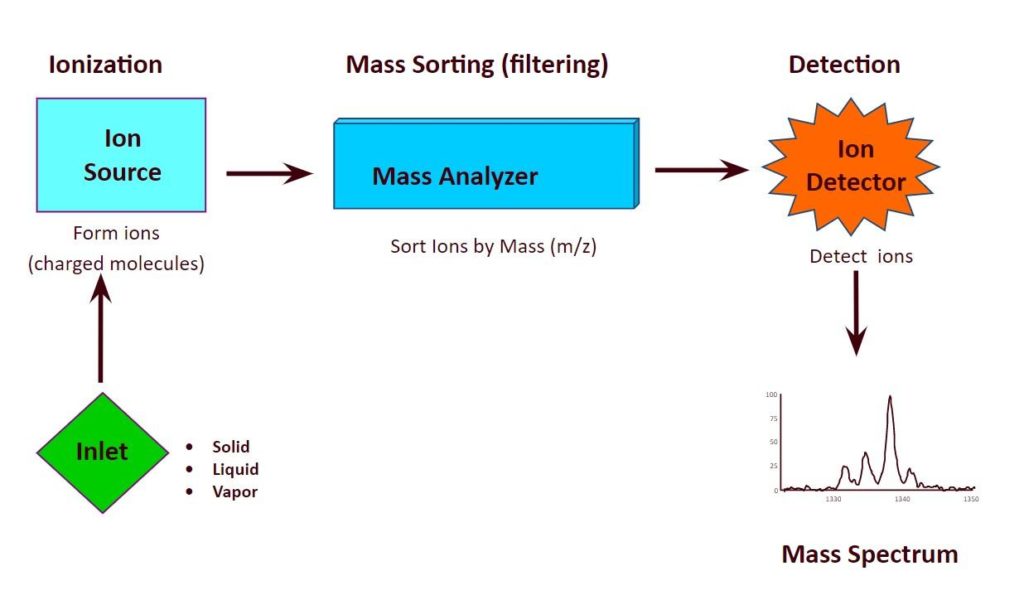
HIGH RESOLUTION MASS SPECTROMETRY
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.
- Molecular weight determination
- Structural characterization
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis of components in a mixture.
Areas of applications:
- Proteomics
- Pharmaceutical analysis
- Forensic analysis
- Environmental analysis
- Clinical applications
ORBITRAP MASS SPECTROMETRY
Orbitrap mass spectrometers deliver a total possible maximum resolution (FWHM) of 1,000,000 at m/z 200 and a sub-1 ppm mass accuracy in a single compact and easy-to-use instrument. These high-resolution accurate-mass systems detect a wide range of compounds and small molecules during both targeted and untargeted analyses, without losing selectivity or sensitivity. Simply put, when it comes to Orbitrap technology, there is no compromise.
High Resolution Mass Spectrometer (HRMS) AT CBA FACILITY
Make: ThermoFisher Scientific
Model: Q Exactive Plus Biopharma Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer

- Resolution up to 240,000 (FWHM) at m/z 200
- Analysis of large molecules up to m/z 8000

Figure 1. The different resolution achievements of Orbitrap instruments compared to Q-TOF mass spectrometers.
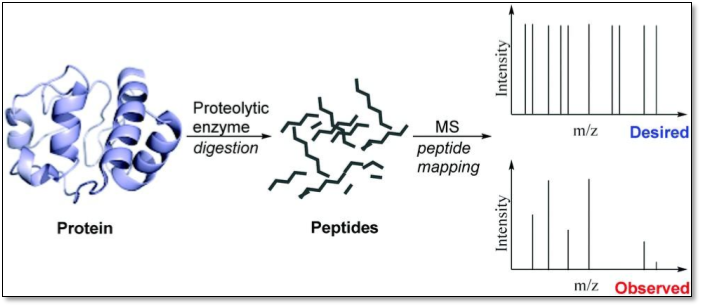
PEPTIDE MAPPING
Peptide mapping is a useful technique for primary structure analysis of proteins. Peptide mapping is usually performed on an isolated protein or a protein mixture. Identifying a protein using peptide mapping requires bottom up approach i.e. digesting the protein into peptides prior to MS analysis.
Although most peptide mapping experiments use trypsin to produce peptides, other enzymes (e.g., Lys-C, Glu-C, etc.) can be used, depending on the experimental requirement. Once digested, the molecular weight of the peptides are acquired.
These experimental masses of the peptides are compared to masses generated from an in silico digest of proteins or translated nucleic acid sequences contained within a database.
GUIDANCE FOR INDUSTRY
- As per ICH Q6B, peptide mapping is important to test for structural characterization and confirmation. The peptide fragments should be identified to the extent possible using techniques such as amino acid compositional analysis, N-terminal sequencing, or mass spectrometry. Peptide mapping of the drug substance or drug product using an appropriately validated procedure is a method that is frequently used to confirm desired product structure for lot release purposes.
- Peptide mapping can also help in identifying Product-related impurities including degradation products
- Peptide mapping is a useful tool to establish similarity between innovator and biosimilar product.
- Peptide mapping has been widely accepted as an identity test for biotherapeutics in the QC lab.
PEPTIDE MAPPING DATA FOR BEVACIZUMAB
The samples were reduced, alkylated and digested using Trypsin protease. The obtained peptides were separated using liquid chromatography(ThermoScientific, Ultimate3000) and eluates were injected into Electro spray ionization mass spectroscopy setup (ThermoScientific, QExactive Orbitrap).
MS and MS/MS data were acquired and compared with the theoretical MS and MS/MS values with mass tolerance of 5 ppm and 15 ppm, respectively using Biopharma finder software (Thermo Fisher).
PEPTIDE MAPPING DATA FOR BEVACIZUMAB

PEPTIDE MAPPING ANALYSIS AT CBA
|
|
Peptide mapping analysis of protein |
| Sample requirement | Amount- 0.1-0.5 ml (10mg/ml) |
| Deliverables | Protein precipitation; protein estimation ; in –solution/in gel enzymatic digestion and peptide sequencing on UPLC-MS (ESI) or nanoESI; blank run; QC sample; protein matching report |
| Information required from Client | Expected molecular weight and formula
Sample solubility, polarity and formulation buffer Concentration Protein sequence in FASTA format for comparison |
